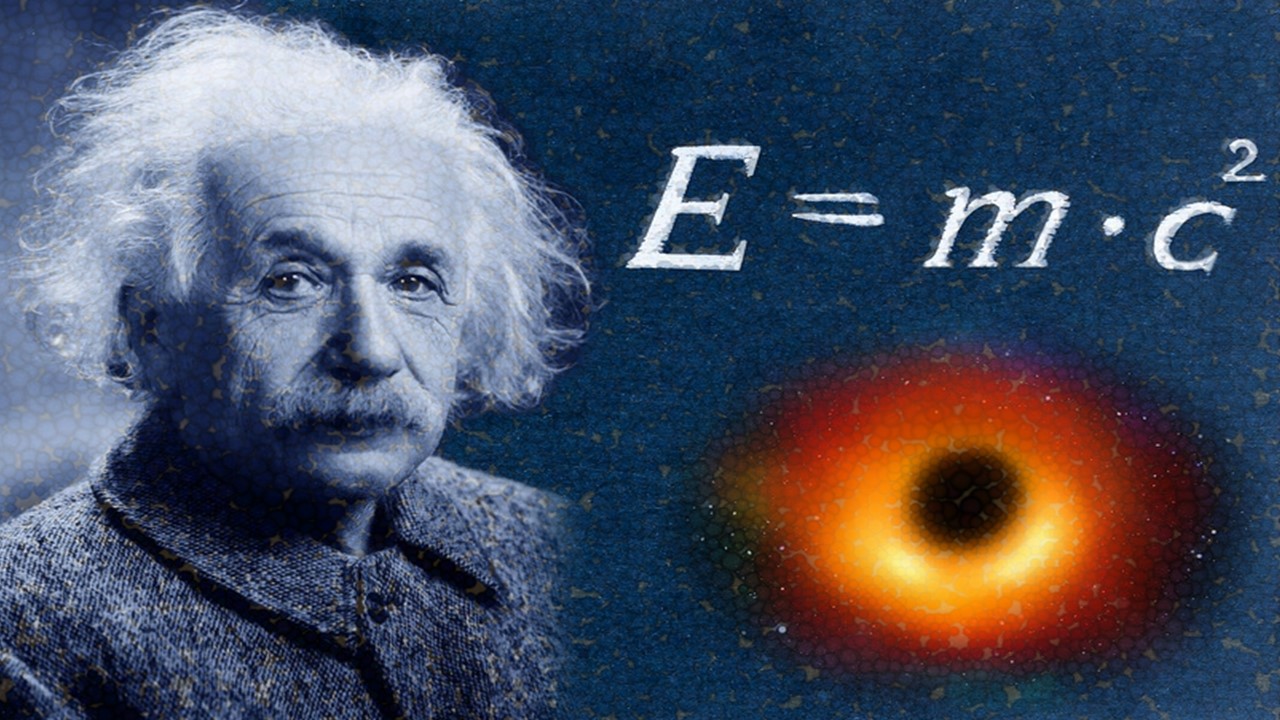Introduction: The Revolutionary Equation
On September 27, 1905, Albert Einstein forever changed the landscape of physics with the publication of his groundbreaking paper on the relationship between energy and mass. This pivotal work introduced the world to the now-iconic equation, E = mc², which stands as one of the most recognized formulas in scientific history. But what does this equation mean, and why is it so revolutionary? Let’s delve into Einstein’s genius and the significance of his discovery.
The Theory Behind E = mc²
At its core, E = mc² represents the relationship between energy (E), mass (m), and the speed of light (c), squared. Einstein’s insight was that mass and energy are interchangeable—mass can be converted into energy and vice versa. This was a radical departure from the classical Newtonian physics that dominated scientific thought at the time. The equation implied that even a small amount of mass could be converted into a huge amount of energy, laying the groundwork for modern physics, including nuclear energy.
The Significance of Einstein’s Work
Einstein’s equation not only transformed our understanding of mass and energy but also laid the foundation for the development of nuclear power and atomic weapons. The ability to convert mass into energy has profound implications in fields ranging from cosmology to particle physics. Without E = mc², many of the technological advances of the 20th and 21st centuries would not have been possible.
A Paradigm Shift in Science
The publication of E = mc² was part of Einstein’s “Annus Mirabilis” or “Miracle Year” in 1905, during which he published four major papers that each revolutionized a different field of physics. Among them, the mass-energy equivalence equation remains one of the most transformative. It challenged the classical physics paradigm and introduced concepts that have led to developments in quantum mechanics and relativity.
Applications of E = mc²
Today, the equation is widely used in various applications. For instance, nuclear power plants utilize the conversion of mass into energy to generate electricity. In astrophysics, the equation helps explain the energy produced by stars, including our sun. Even the devastating power of atomic bombs is a result of the energy released by the conversion of mass into energy, as explained by Einstein’s formula.
A Lasting Legacy
Einstein’s E = mc² continues to inspire scientists and physicists across the globe. His work symbolizes the profound link between theory and application, showing how abstract scientific ideas can lead to practical technologies that shape human history. “Energy and mass are the same thing,” Einstein said, explaining his simple yet powerful equation that forever altered our understanding of the universe.
“As far as the laws of mathematics refer to reality, they are not certain; and as far as they are certain, they do not refer to reality.” – Albert Einstein
Conclusion:
Albert Einstein’s 1905 paper, introducing the equation E = mc², remains one of the most influential scientific works ever published. Its profound implications not only advanced theoretical physics but also played a key role in shaping modern technology and our understanding of the universe. Einstein’s genius continues to resonate today, proving the timeless value of scientific exploration and discovery.